what is the best command to use to view the router s interface status and protocol status?
New Version:
1. Which dynamic routing protocol was adult to interconnect different Internet service providers?
- BGP*
- EIGRP
- OSPF
- RIP
ii. Which routing protocol is express to smaller network implementations because it does not accommodate growth for larger networks?
- OSPF
- RIP*
- EIGRP
- IS-IS
3. What two tasks do dynamic routing protocols perform? (Choose ii.)
- discover hosts
- update and maintain routing tables*
- propagate host default gateways
- network discovery*
- assign IP addressing
4. When would information technology be more benign to use a dynamic routing protocol instead of static routing?
- in an organization with a smaller network that is not expected to grow in size
- on a stub network that has a single exit point
- in an arrangement where routers endure from functioning issues
- on a network where at that place is a lot of topology changes*
v. When would it be more than benign to utilize static routing instead of dynamic routing protocols?
- on a network where dynamic updates would pose a security risk*
- on a network that is expected to continually grow in size
- on a network that has a large amount of redundant paths
- on a network that unremarkably experiences link failures
vi. What is a purpose of the network command when configuring RIPv2 every bit the routing protocol?
- It identifies the interfaces that vest to a specified network.*
- Information technology specifies the remote network that can now be reached.
- It immediately advertises the specified network to neighbor routers with a classful mask.
- Information technology populates the routing table with the network entry.
7. A network administrator configures a static route on the edge router of a network to assign a gateway of last resort. How would a network administrator configure the edge router to automatically share this road within RIP?
- Use the auto-summary command.
- Use the passive-interface control.
- Use the network command.
- Use the default-data originate control.*
8. What is the purpose of the passive-interface control?
- allows a routing protocol to frontward updates out an interface that is missing its IP address
- allows a router to send routing updates on an interface but not receive updates via that interface
- allows an interface to remain up without receiving keepalives
- allows interfaces to share IP addresses
- allows a router to receive routing updates on an interface only not send updates via that interface*
nine. Which route would exist automatically created when a router interface is activated and configured with an IP accost?
- D 10.16.0.0/24 [90/3256] via 192.168.6.9
- C 192.168.0.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet 0/0*
- S 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet 0/1
- O 172.16.0.0/16 [110/65] via 192.168.five.one
10. Refer to the exhibit. Which ii types of routes could be used to describe the 192.168.200.0/xxx route? (Cull two.)
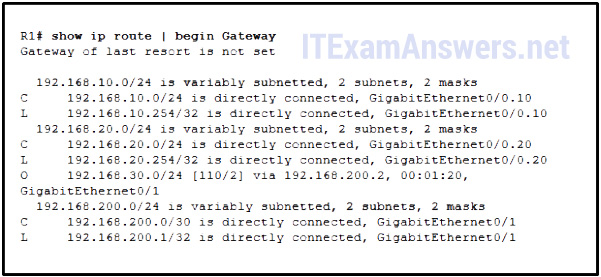
- ultimate route*
- level 1 parent route
- level 1 network route
- level ii child route*
- supernet route
eleven. What occurs side by side in the router lookup process afterward a router identifies a destination IP address and locates a matching level 1 parent road?
- The level 2 child routes are examined.*
- The level ane supernet routes are examined.
- The level 1 ultimate routes are examined.
- The router drops the package.
12. Which route would be used to forward a packet with a source IP address of 192.168.10.1 and a destination IP address of 10.1.1.i?
- C 192.168.10.0/xxx is straight connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
- Southward ten.1.0.0/xvi is straight connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
- O x.1.1.0/24 [110/65] via 192.168.200.2, 00:01:twenty, Serial0/1/0*
- S* 0.0.0.0/0 [ane/0] via 172.16.1.1
13. Which 2 requirements are used to decide if a route can be considered as an ultimate route in a router's routing table? (Cull 2.)
- contain subnets
- be a default route
- contain an go out interface*
- exist a classful network entry
- contain a next-hop IP address*
14. What is a disadvantage of using dynamic routing protocols?
- They are simply suitable for elementary topologies.
- Their configuration complication increases equally the size of the network grows.
- They send messages about network condition insecurely across networks by default.*
- They crave administrator intervention when the pathway of traffic changes.
15. Which two statements are true regarding classless routing protocols? (Choose 2.)
- sends subnet mask information in routing updates*
- sends consummate routing table update to all neighbors
- is supported past RIP version one
- allows for use of both 192.168.1.0/thirty and 192.168.1.16/28 subnets in the aforementioned topology*
- reduces the amount of address infinite available in an organization
16. Refer to the exhibit. Based on the fractional output from the bear witness ip route command, what two facts can exist adamant about the RIP routing protocol? (Choose ii.)
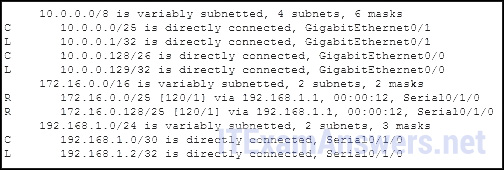
- RIP version two is running on this router and its RIP neighbor.*
- The metric to the network 172.sixteen.0.0 is 120.
- RIP version one is running on this router and its RIP neighbor.
- The command no machine-summary has been used on the RIP neighbour router.*
- RIP volition annunciate ii networks to its neighbor.
17. While configuring RIPv2 on an enterprise network, an engineer enters the command network 192.168.10.0 into router configuration mode. What is the result of entering this command?
- The interface of the 192.168.10.0 network is sending version 1 and version 2 updates.
- The interface of the 192.168.10.0 network is receiving version i and version 2 updates.
- The interface of the 192.168.10.0 network is sending only version 2 updates.*
- The interface of the 192.168.10.0 network is sending RIP howdy messages.
eighteen. A destination route in the routing table is indicated with a lawmaking D. Which kind of route entry is this?
- a static route
- a road used as the default gateway
- a network directly connected to a router interface
- a route dynamically learned through the EIGRP routing protocol*
xix. Refer to the exhibit. Which interface will exist the go out interface to forward a data bundle with the destination IP address 172.sixteen.0.66?
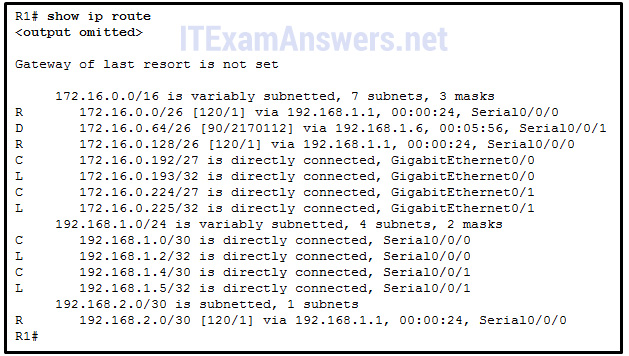
- Serial0/0/0
- Serial0/0/one*
- GigabitEthernet0/0
- GigabitEthernet0/1
20. Which type of route will require a router to perform a recursive lookup?
- an ultimate route that is using a next hop IP address on a router that is not using CEF*
- a level 2 child route that is using an exit interface on a router that is non using CEF
- a level 1 network route that is using a adjacent hop IP address on a router that is using CEF
- a parent route on a router that is using CEF
21. Which route is the best match for a bundle entering a router with a destination address of 10.16.0.two?
- S 10.0.0.0/viii [ane/0] via 192.168.0.2
- S ten.16.0.0/24 [ane/0] via 192.168.0.9*
- S 10.sixteen.0.0/sixteen is directly connected, Ethernet 0/1
- South x.0.0.0/16 is directly connected, Ethernet 0/0
22. A router is configured to participate in multiple routing protocol: RIP, EIGRP, and OSPF. The router must transport a bundle to network 192.168.14.0. Which road will be used to frontward the traffic?
- a 192.168.14.0/26 route that is learned via RIP*
- a 192.168.14.0/24 road that is learned via EIGRP
- a 192.168.14.0/25 road that is learned via OSPF
- a 192.168.fourteen.0/25 route that is learned via RIP
23. What is unlike between IPv6 routing table entries compared to IPv4 routing tabular array entries?
- IPv6 routing tables include local route entries which IPv4 routing tables do non.
- By design IPv6 is classless so all routes are finer level i ultimate routes.*
- The selection of IPv6 routes is based on the shortest matching prefix, unlike IPv4 route option which is based on the longest matching prefix.
- IPv6 does non apply static routes to populate the routing table every bit used in IPv4.
24. Match the dynamic routing protocol component to the characteristic. (Non all options are used.)
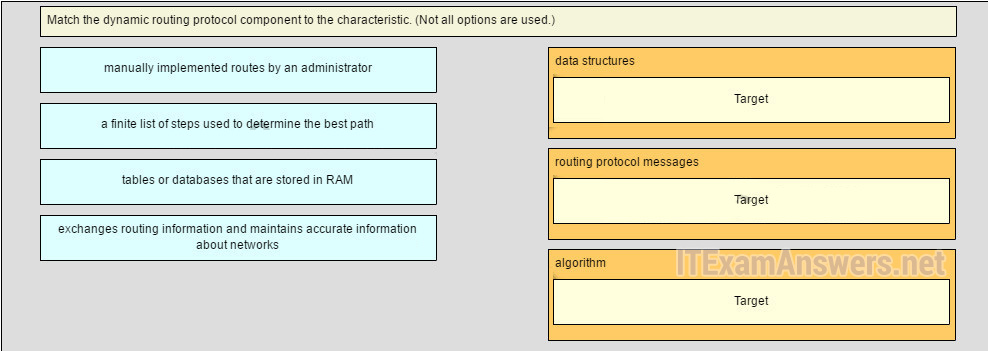
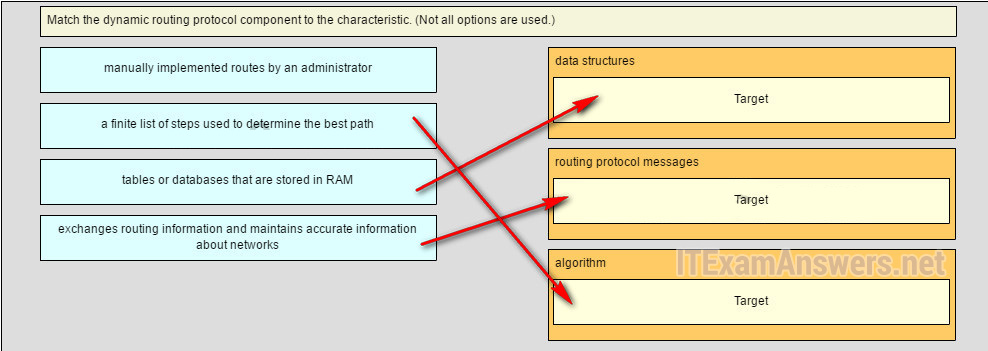
data structures
tables or databases that are stored in RAM*
routing protocol letters
exchanges routing information and maintains accurate information almost networks*
algorithm
a finite list of steps used to determine the best path*
25. Match the characteristic to the respective blazon of routing. (Not all options are used.)
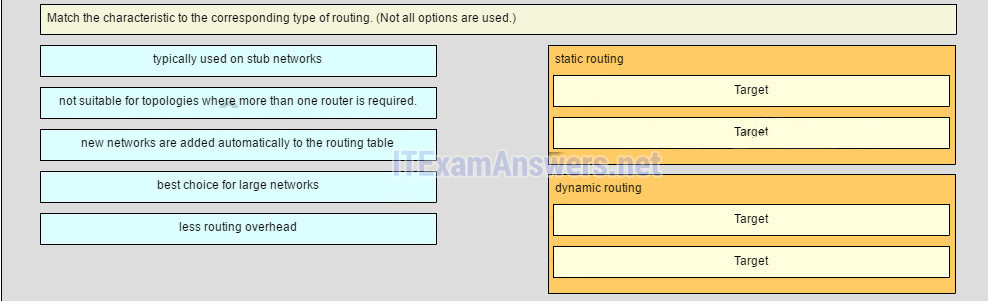
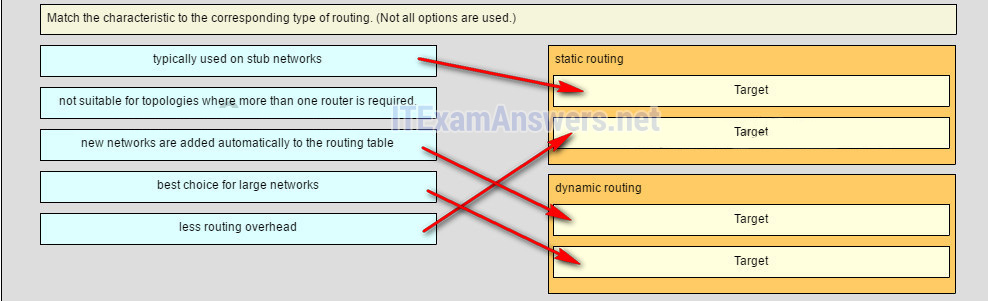
Place the options in the post-obit order:
[+] typically used on stub networks *
[+] less routing overhead *
[#] new networks are added automatically to the routing table *
[#] best choice for large networks*
Older Version:
26. Which iii statements accurately describe VLAN types? (Choose three).
- A management VLAN is any VLAN that is configured to access direction features of the switch.*
- A data VLAN is used to carry VLAN management information and user-generated traffic.
- After the initial boot of an unconfigured switch, all ports are members of the default VLAN. *
- An 802.1Q trunk port, with a native VLAN assigned, supports both tagged and untagged traffic.*
- Voice VLANs are used to back up user phone and e-mail service traffic on a network.
- VLAN one is ever used as the management VLAN.
27. Which type of VLAN is used to designate which traffic is untagged when crossing a trunk port?
- data
- default
- native*
- direction
28. What are three primary benefits of using VLANs? (Choose 3.)
- security*
- a reduction in the number of torso links
- cost reduction *
- end user satisfaction
- improved Information technology staff efficiency*
- no required configuration
29. Refer to the showroom. A frame is traveling between PC-A and PC-B through the switch. Which argument is truthful apropos VLAN tagging of the frame?
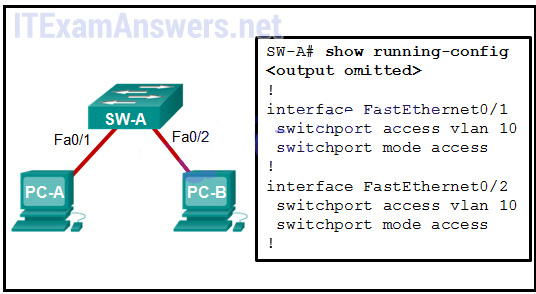
- A VLAN tag is added when the frame leaves PC-A.
- A VLAN tag is added when the frame is accepted by the switch.
- A VLAN tag is added when the frame is forwarded out the port to PC-B.
- No VLAN tag is added to the frame.*
xxx. Which command displays the encapsulation type, the vocalism VLAN ID, and the access mode VLAN for the Fa0/one interface?
- testify vlan brief
- show interfaces Fa0/1 switchport*
- testify mac address-table interface Fa0/1
- bear witness interfaces trunk
31. What must the network ambassador do to remove Fast Ethernet port fa0/1 from VLAN 2 and assign it to VLAN three?
- Enter the no vlan two and the vlan 3 commands in global configuration mode.
- Enter the switchport access vlan iii control in interface configuration fashion.*
- Enter the switchport trunk native vlan 3 command in interface configuration fashion.
- Enter the no shutdown in interface configuration style to return it to the default configuration and then configure the port for VLAN 3.
32. A Cisco Catalyst switch has been added to back up the utilise of multiple VLANs as part of an enterprise network. The network technician finds it necessary to articulate all VLAN information from the switch in social club to comprise a new network blueprint. What should the technician practice to achieve this chore?
- Erase the startup configuration and reboot the switch.
- Erase the running configuration and reboot the switch.
- Delete the startup configuration and the vlan.dat file in the wink retentivity of the switch and reboot the switch.*
- Delete the IP accost that is assigned to the management VLAN and reboot the switch.
33. Which two characteristics match extended range VLANs? (Choose two.)
- CDP can be used to acquire and store these VLANs.
- VLAN IDs exist between 1006 to 4094. *
- They are saved in the running-config file by default.*
- VLANs are initialized from flash memory.
- They are commonly used in small networks.
34. What happens to switch ports after the VLAN to which they are assigned is deleted?
- The ports are disabled.
- The ports are placed in trunk mode.
- The ports are assigned to VLAN1, the default VLAN.
- The ports finish communicating with the attached devices.*
35. A Cisco switch currently allows traffic tagged with VLANs 10 and 20 across trunk port Fa0/v. What is the effect of issuing a switchport trunk allowed vlan xxx command on Fa0/5?
- Information technology allows VLANs 1 to 30 on Fa0/5.
- It allows VLANs 10, xx, and 30 on Fa0/5.
- It allows only VLAN 30 on Fa0/v.*
- It allows a native VLAN of xxx to be implemented on Fa0/5.
36. What VLANs are allowed beyond a body when the range of allowed VLANs is gear up to the default value?
- All VLANs will exist allowed across the trunk.*
- Only VLAN one will be immune across the trunk.
- Only the native VLAN will be allowed across the trunk.
- The switches will negotiate via VTP which VLANs to permit across the trunk.
37. Which command should the network administrator implement to prevent the transfer of DTP frames betwixt a Cisco switch and a non-Cisco switch?
- S1(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
- S1(config-if)# switchport nonegotiate*
- S1(config-if)# switchport mode dynamic desirable
- S1(config-if)# switchport mode access
- S1(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan none
38. Under which two occasions should an ambassador disable DTP while managing a local area network? (Choose ii.)
- when connecting a Cisco switch to a non-Cisco switch*
- when a neighbour switch uses a DTP mode of dynamic auto
- when a neighbor switch uses a DTP mode of dynamic desirable
- on links that should not exist trunking*
- on links that should dynamically effort trunking
39. In a bones VLAN hopping attack, which switch feature practise attackers have reward of?
- an open up Telnet connection
- automatic encapsulation negotiation
- forwarding of broadcasts
- the default automated trunking configuration*
40. Which two Layer 2 security best practices would help prevent VLAN hopping attacks? (Choose two.)
- Alter the native VLAN number to one that is distinct from all user VLANs and is not VLAN 1.*
- Change the management VLAN to a distinct VLAN that is not attainable by regular users.
- Statically configure all ports that connect to cease-user host devices to be in torso mode.
- Disable DTP autonegotiation on terminate-user ports.*
- Apply SSH for all remote direction admission.
41. Refer to the exhibit. Interface Fa0/i is continued to a PC. Fa0/2 is a body link to another switch. All other ports are unused. Which security best practice did the administrator forget to configure?
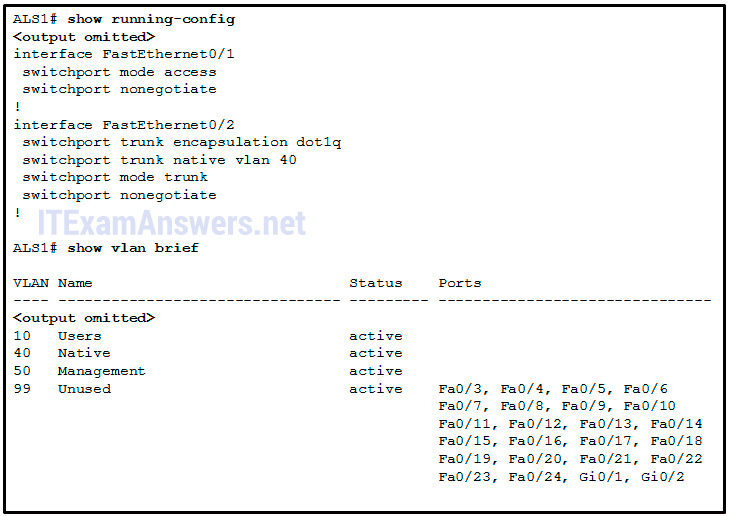
- Disable autonegotiation and prepare ports to either static admission or static trunk.
- Change the native VLAN to a stock-still VLAN that is distinct from all user VLANs and to a VLAN number that is non VLAN 1.
- Configure all unused ports to a 'black-hole' VLAN that is not used for annihilation on the network.
- All user ports are associated with VLANs distinct from VLAN 1 and singled-out from the 'black-hole' VLAN.*
42. A network ambassador is determining the best placement of VLAN torso links. Which two types of bespeak-to-point connections utilise VLAN trunking? (Cull 2.)
- between ii switches that use multiple VLANs*
- betwixt a switch and a client PC
- between a switch and a server that has an 802.1Q NIC*
- between a switch and a network printer
- between 2 switches that share a mutual VLAN
43. What is the effect of issuing a switchport access vlan xx command on the Fa0/18 port of a switch that does non accept this VLAN in the VLAN database?
- The command will take no upshot on the switch.
- VLAN 20 volition exist created automatically.*
- An fault stating that VLAN twenty does non exist will exist displayed and VLAN twenty is non created.
- Port Fa0/eighteen will be shut downwards.
44. Port Fa0/11 on a switch is assigned to VLAN 30. If the control no switchport admission vlan xxx is entered on the Fa0/xi interface, what will happen?
- Port Fa0/11 volition exist shutdown.
- An error message would be displayed.
- Port Fa0/eleven will exist returned to VLAN 1.*
- VLAN 30 will be deleted.
45. Which command is used to remove merely VLAN 20 from a switch?
- delete vlan.dat
- delete flash:vlan.dat
- no vlan 20 *
- no switchport access vlan 20
46. Refer to the exhibit. PC-A and PC-B are both in VLAN sixty. PC-A is unable to communicate with PC-B. What is the trouble?
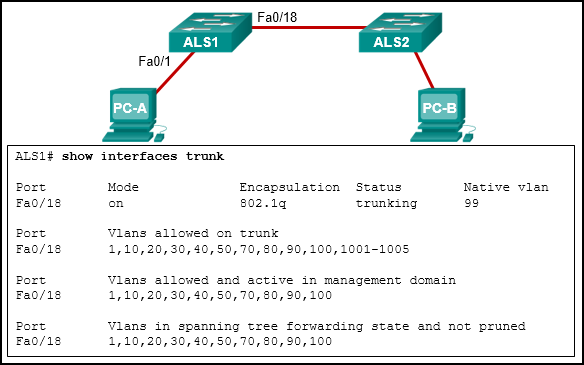
CCNA 2 Chapter 3 Exam Answer 002 (v5.02, 2015)
- The native VLAN should be VLAN lx.
- The native VLAN is being pruned from the link.
- The torso has been configured with the switchport nonegotiate command.
- The VLAN that is used by PC-A is not in the list of allowed VLANs on the body.*
47. What happens to a port that is associated with VLAN 10 when the ambassador deletes VLAN 10 from the switch?
- The port becomes inactive.*
- The port goes dorsum to the default VLAN.
- The port automatically assembly itself with the native VLAN.
- The port creates the VLAN once again.
48. In a basic VLAN hopping attack, which switch feature practise attackers take advantage of?
- an open Telnet connection
- automatic encapsulation negotiation
- forwarding of broadcasts
- the default automatic trunking configuration*
49. Which two Layer 2 security best practices would help prevent VLAN hopping attacks? (Cull 2.)
- Modify the native VLAN number to one that is distinct from all user VLANs and is non VLAN 1.*
- Alter the direction VLAN to a singled-out VLAN that is not attainable past regular users.
- Statically configure all ports that connect to stop-user host devices to be in body mode.
- Disable DTP autonegotiation on end-user ports.*
- Use SSH for all remote management access.
50. Refer to the exhibit. Interface Fa0/1 is connected to a PC. Fa0/2 is a body link to another switch. All other ports are unused. Which security all-time practise did the ambassador forget to configure?
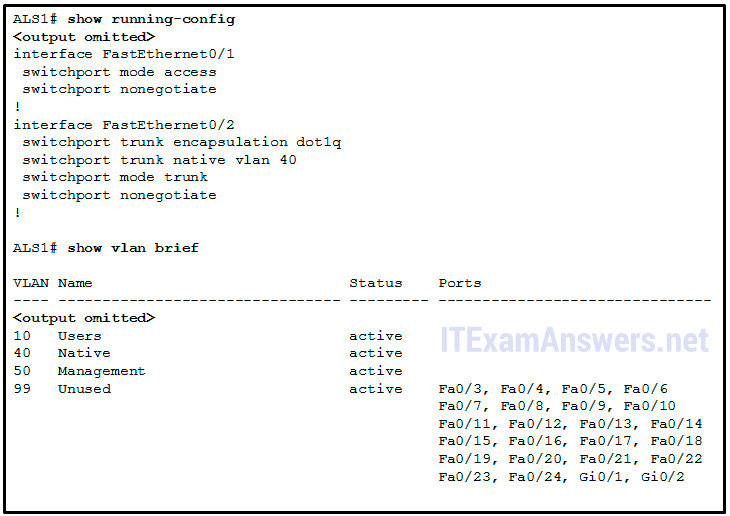
- Disable autonegotiation and prepare ports to either static access or static trunk.
- Change the native VLAN to a fixed VLAN that is distinct from all user VLANs and to a VLAN number that is not VLAN 1.
- Configure all unused ports to a 'blackness-hole' VLAN that is not used for anything on the network.
- All user ports are associated with VLANs distinct from VLAN 1 and distinct from the 'black-hole' VLAN.*
51. A network administrator is determining the all-time placement of VLAN trunk links. Which 2 types of signal-to-point connections utilize VLAN trunking? (Choose two.)
- between two switches that share a common VLAN
- between a switch and a server that has an 802.1Q NIC*
- between a switch and a client PC
- between a switch and a network printer
- between two switches that utilize multiple VLANs*
52. What happens to a port that is associated with VLAN ten when the administrator deletes VLAN 10 from the switch?
- The port automatically associates itself with the native VLAN.
- The port creates the VLAN again.
- The port goes dorsum to the default VLAN.
- The port becomes inactive.*
53. Refer to the exhibit. Interface Fa0/i is continued to a PC. Fa0/2 is a torso link to another switch. All other ports are unused. Which security best practice did the administrator forget to configure?
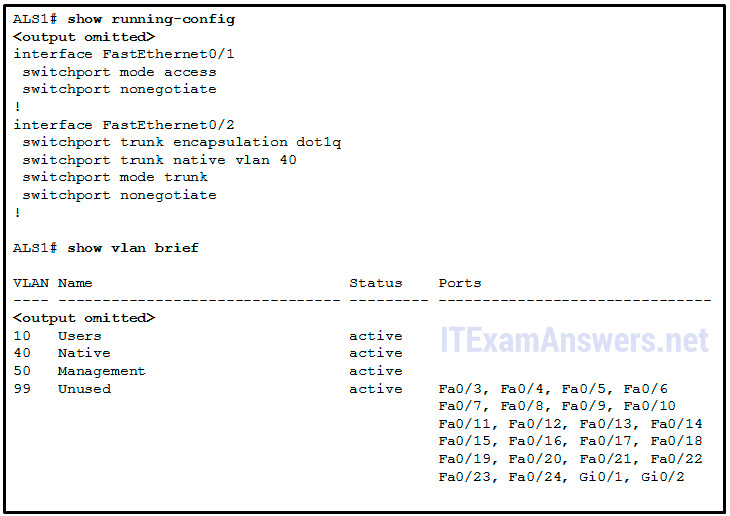
- Configure all unused ports to a 'black-pigsty' VLAN that is not used for anything on the network.
- Disable autonegotiation and set ports to either static admission or static trunk.
- Change the native VLAN to a fixed VLAN that is distinct from all user VLANs and to a VLAN number that is not VLAN 1.
- All user ports are associated with VLANs distinct from VLAN ane and singled-out from the 'blackness-pigsty' VLAN.*
54. Which command is used to remove simply VLAN xx from a switch?
- no switchport access vlan 20
- delete wink:vlan.dat
- no vlan xx*
- delete vlan.dat
55. What is the effect of issuing a switchport admission vlan 20 command on the Fa0/18 port of a switch that does not have this VLAN in the VLAN database?
- VLAN 20 will be created automatically.*
- The command will have no consequence on the switch.
- Port Fa0/eighteen volition be close down.
- An error stating that VLAN 20 does not exist will be displayed and VLAN 20 is not created.
56. Identify the options in the post-obit order:
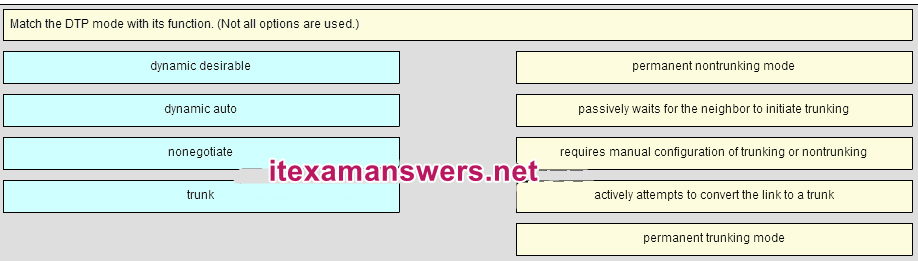
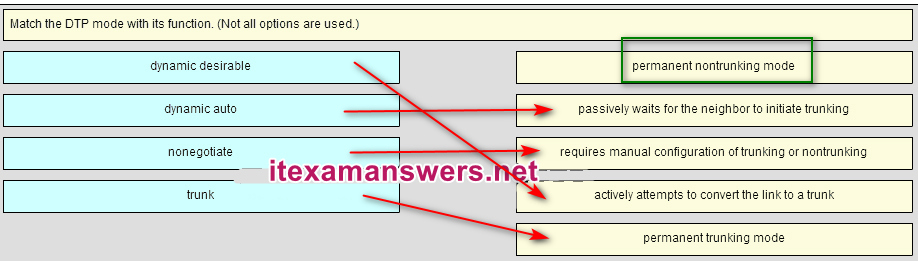
– not scored –
dynamic auto
nonegotiate
dynamic desirable
trunk
57. Port Fa0/xi on a switch is assigned to VLAN xxx. If the command no switchport access vlan 30 is entered on the Fa0/11 interface, what will happen?
- Port Fa0/eleven will be returned to VLAN 1.*
- VLAN 30 will exist deleted.
- An error message would be displayed.
- Port Fa0/11 volition exist shutdown.
58. Which 2 Layer ii security all-time practices would assistance prevent VLAN hopping attacks? (Choose ii.)
- Disable DTP autonegotiation on end-user ports.*
- Change the direction VLAN to a distinct VLAN that is not attainable by regular users.
- Statically configure all ports that connect to stop-user host devices to be in trunk style.
- Change the native VLAN number to one that is distinct from all user VLANs and is non VLAN i.*
- Utilize SSH for all remote management admission.
59. In a basic VLAN hopping assault, which switch feature exercise attackers take advantage of?
- automatic encapsulation negotiation
- the default automatic trunking configuration*
- an open up Telnet connectedness
- forwarding of broadcasts
60. Refer to the exhibit. PC-A and PC-B are both in VLAN 60. PC-A is unable to communicate with PC-B. What is the problem?
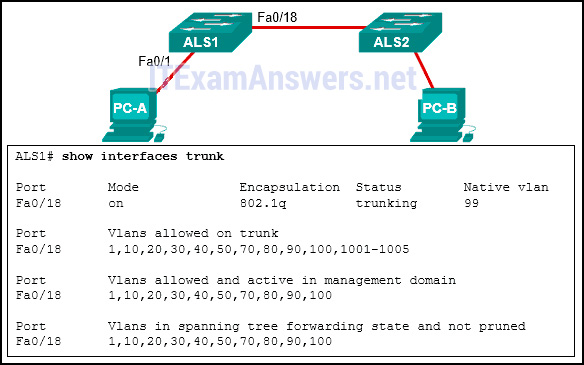
- The native VLAN is existence pruned from the link.
- The VLAN that is used by PC-A is not in the list of immune VLANs on the torso.*
- The trunk has been configured with the switchport nonegotiate command.
- The native VLAN should be VLAN 60.
61. Under which two occasions should an administrator disable DTP while managing a local area network? (Choose two.)
- when a neighbor switch uses a DTP mode of dynamic desirable
- on links that should dynamically attempt trunking
- when connecting a Cisco switch to a non-Cisco switch*
- when a neighbor switch uses a DTP mode of dynamic auto
- on links that should not be trunking*
62. Open up the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activeness instructions so answer the question.
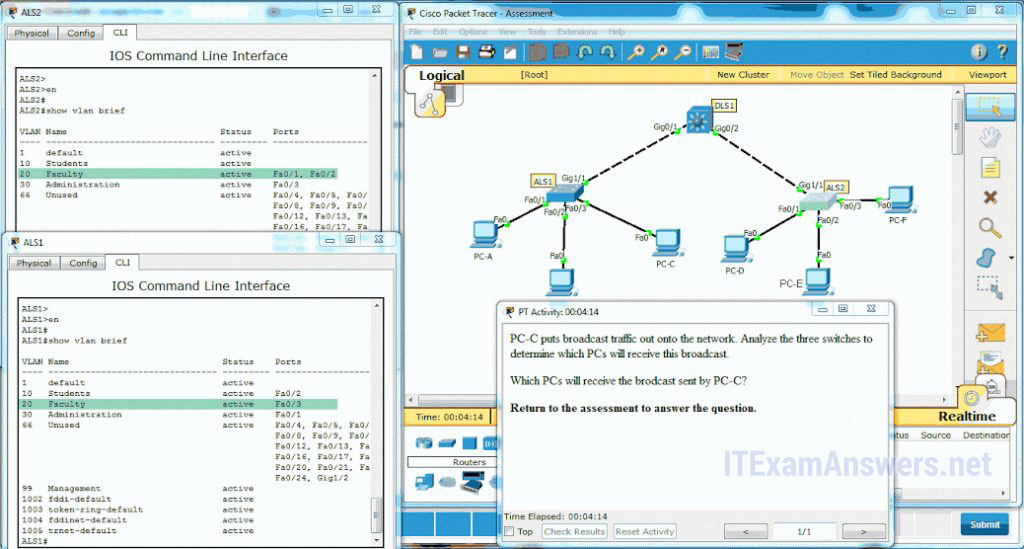
Which PCs will receive the broadcast sent past PC-C?
- PC-D, PC-E*
- PC-A, PC-B, PC-D, PC-E
- PC-A, PC-B
- PC-A, PC-B, PC-D, PC-Due east, PC-F
- PC-A, PC-B, PC-E
63. Which 2 statements are true near VLAN implementation? (Cull two.)
- The network load increases significantly considering of added trunking information.
- Devices in one VLAN do non hear the broadcasts from devices in another VLAN.*
- The size of the collision domain is reduced.
- VLANs logically grouping hosts, regardless of physical location.*
- The number of required switches in a network decreases.
64. Which switch feature ensures that no unicast, multicast, or broadcast traffic is passed between ports that are configured with this feature?
- switch port security
- PVLAN protected port*
- ACL
- VLAN
65. Fill in the blank. Employ the full command syntax.
The " show vlan brief* " command displays the VLAN assignment for all ports as well equally the existing VLANs on the switch.
66. Which combination of DTP modes assault side by side Cisco switches volition cause the link to become an admission link instead of a torso link?
- dynamic auto – dynamic auto*
- dynamic desirable – dynamic desirable
- dynamic desirable – trunk
- dynamic desirable – dynamic auto
67. An administrator has adamant that the traffic from a switch that corresponds to a VLAN is non being received on some other switch over a trunk link. What could be the problem?
- trunk mode mismatch
- allowed VLANS on trunks*
- native VLANS mismatch
- dynamic desirable mode on i of the trunk links
68. What is the default DTP mode on Cisco 2960 and 3560 switches?
- body
- dynamic auto*
- admission
- dynamic desirable
69. Refer to the exhibit.

What tin exist determined from the output that is shown?
- Interface FastEthernet 0/1 is configured with the switchport protected command.*
- Interface FastEthernet 0/one is configured with the nonegotiate keyword.
- Interface FastEthernet 0/1 is trunking and using Native VLAN 1.
- Interface FastEthernet 0/1 is configured as dynamic machine by the administrator.
lxx. Match the IEEE 802.1Q standard VLAN tag field in the clarification. (not all options are used)

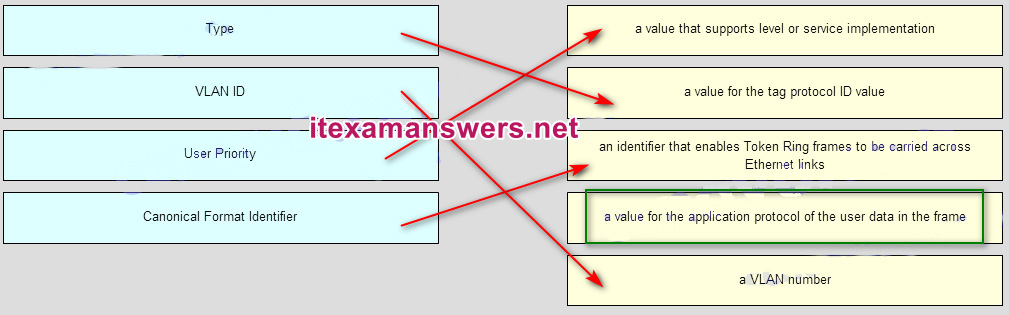 Place the options in the following order:
Place the options in the following order:
User Priority – value that supports level or service implementation
Blazon – value for the tag protocol ID value
Canonical Format Identifier – identifier that enables Token Ring frames to be carried across Ethernet Links
– not scored – -value for the awarding protocol of the user data in a frame*
VLAN ID – VLAN number
71. Which ii modes does Cisco recommend when configuring a particular switch port? (Choose 2.)
- body*
- IEEE 802.1Q
- access*
- Gigabit Ethernet
- FastEthernet
- ISL
Download PDF File below:
[sociallocker id="54558″]
[/sociallocker]
Source: https://itexamanswers.net/ccna-2-v5-0-3-v6-0-chapter-3-exam-answers-100-full.html
0 Response to "what is the best command to use to view the router s interface status and protocol status?"
Post a Comment